Lead acid battery (VRLA), an electrode made primarily of lead and its oxides, is an accumulator of sulfuric acid solution.Lead dioxide is the main component of the positive electrode and lead is the main component of the negative electrode.Lead sulfate is the main component of anode and cathode in charge state.
A single-grid lead-acid battery has a nominal voltage of 2.0v and can discharge to 1.5v and charge to 2.4v.In applications, 6 single-grid lead-acid batteries are often used in series to form the 12V lead-acid battery, and 24V, 36V, 48V and so on.
Generation of electromotive force of lead-acid battery
(1) after the lead-acid battery charging, the positive plate is lead dioxide (PbO2), under the action of water molecules in sulfuric acid solution, a small amount of lead dioxide and natural water dissociation of volatile substances - hydrogen dioxide (Pb (OH) 4), hydroxyl ions in solution, the lead ions (Pb) on the positive plate, so the positive plate on the lack of electrons.
(2) after the lead-acid battery is charged, the negative plate is lead (Pb), which reacts with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) in the electrolyte to form lead ions (Pb2), lead ions are transferred to the electrolyte, and extra two electrons (2e) are left on the negative plate.
(3) it can be seen that when the external circuit is not connected (the battery is open), due to chemical action, the positive plate lacks electrons, and the extra electrons on the blessing plate produce a certain potential difference, which is the electromotive force of the battery.
Electrochemical reaction of lead-acid battery discharge process
(1) when the lead-acid battery is discharging, under the action of potential difference of the battery, electrons on the negative plate enter into the positive plate through the load to form current I.Chemical reactions take place inside the battery.
(2) after each lead atom on the negative plate gives off two electrons, the lead ions (Pb2) are born and the sulfate ions in the electrolyte (SO4?2) reaction, on the plate born insoluble lead sulfate (PbSO4).
(3) the lead ion (Pb4) of the positive plate obtains two electrons (2e) from the negative electrode, which becomes the lead ion (Pb2) and the sulfate ion (SO4?2) reaction, on the plate born insoluble lead sulfate (PbSO4).Oxygen ions (O?2) react with the hydrogen ion (H) in the electrolyte to produce stable water.
(4) under the action of the electric field, the sulfate ions and hydrogen ions existing in the electrolyte move to the positive and negative poles of the battery respectively, forming a current inside the battery, forming the whole circuit, and the battery continues to discharge outward.
(5) when discharging, the concentration of H2SO4 decreases continuously, the lead sulfate (PbSO4) on the anode and cathode increases, the internal resistance of the battery increases (lead sulfate does not conduct electricity), the concentration of electrolyte decreases, and the electromotive force of the battery decreases.
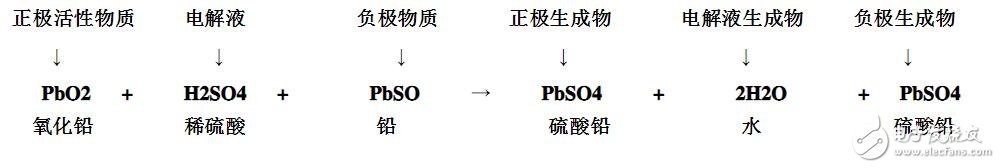
(6) the chemical reaction formula is:

Electrochemical reaction of lead-acid battery charging process
(1) when charging, should be in the external flow of power (charge pole or rectifier), so that positive and negative plate after discharge natural substances back to the original active substances, and the external electrical energy into chemical energy storage.
(2) on the positive plate under the action of external current, lead sulfate by dissociation of bivalent lead ions (Pb2) and sulfate anion (SO4-2) due to external power constantly draw electrons from the anode, the positive plate around free of lead (ii) (Pb2) continuously released two electrons to complement, become a tetravalent lead ions (Pb4), and react with water to continue, the ultimate natural lead dioxide on the positive plate (PbO2).
(3) in the negative plate, under the action of external current, lead sulfate is dissociated into divalent lead ion (Pb2) and sulfate negative ion (SO4 ~ 2), because the negative electrode continues to obtain electrons from the external power source, the free divalent lead ion (Pb2) around the negative plate is neutralized into lead (Pb), and attached to the negative plate with flecy lead.
(4) in the electrolyte and the anode are free of hydrogen ions (H) and sulfuric acid root ion (SO4  ̄ 2), the cathode constantly produce sulfuric acid root ion (SO4  ̄ 2), under the action of electric field, the hydrogen ions move to the cathode, sulfuric acid root ion to the positive movement, the formation of current.
(5) at the later stage of charging, water electrolysis reaction will occur in the solution under the action of external current.
(6) the chemical reaction formula is:
Changes of electrolyte of lead-acid battery after charging and discharging
(1) it can be seen from the above that when the lead battery is discharged, the sulfuric acid in the electrolyte decreases continuously, the water increases gradually, and the specific gravity of the solution decreases.
(2) it can be seen from the above that when the lead-acid battery is charged, the sulfuric acid in the electrolyte increases continuously, the water decreases gradually, and the specific gravity of the solution increases.
(3) in practical work, the charging degree of lead-acid battery can be determined according to the change of electrolyte specific gravity.(ritz battery)

 Английский
Английский  Китайский
Китайский  Немецкий
Немецкий  Корейский
Корейский  Японский
Японский  Farsi
Farsi  Portuguese
Portuguese  Russian
Russian  Испанский
Испанский 





