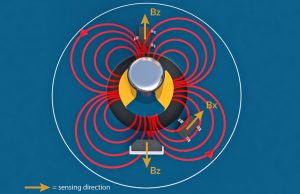
What's a sensor?
Sensor is a detection device, which can feel the measured information and transform the perceived information into electrical signal or other required form of information output in accordance with certain rules, so as to meet the requirements of information transmission, processing, storage, display, record and control.
The characteristics of sensors include miniaturization, digitization, intelligentization, multi-function, systematization and networking.It is the first step to realize automatic detection and automatic control.With the existence and development of sensors, objects have senses such as touch, taste and smell, and slowly become alive.According to its basic sensing function, it is usually divided into 10 categories, such as thermal sensor, light sensor, air sensor, force sensor, magnetic sensor, humidity sensor, sound sensor, radiation sensor, color sensor and taste sensor.
Composition of sensor
The sensor generally consists of four parts: sensing element, conversion element, conversion circuit and auxiliary power supply.
The sensor directly senses the measured physical quantity and outputs the measured physical quantity signal.The conversion element converts the physical quantity signals output by the sensitive element into electrical signals;The conversion circuit is responsible for amplifying and modulating the output electrical signals of the conversion element.Auxiliary power supply is also required for conversion elements and circuits.
Types of sensors
1. The resistance type
A resistive sensor is a device that converts physical quantities such as displacement, deformation, force, acceleration, humidity, temperature, etc. into resistance values.The main resistance strain type, piezoresistance type, thermal resistance, thermal sensitivity, gas sensitivity, moisture sensitivity and other resistance sensor parts.
2. Frequency conversion power
Frequency conversion power sensor based on the input voltage, current signal to communicate sampling, then samples values through cable, optical fiber transmission system are connected to the digital quantity input secondary instrument, digital quantity input secondary instrument to the operations of the sampling values of the voltage, current, voltage RMS, current RMS can be gained, the fundamental voltage, the fundamental wave current, harmonic voltage and harmonic current, active power, power of fundamental wave and harmonic power of parameters.
3. The weighing
Weighing sensor is a force - to - electricity conversion device which can convert gravity into electrical signal

4. Thermal resistance
Thermal resistance temperature measurement is based on the metal conductor resistance value increases with the increase of temperature to measure the temperature.Most thermal resistances are made of pure metal materials.It is divided into positive temperature coefficient sensor and negative temperature coefficient sensor.
5. The laser
A sensor that USES laser technology to make measurements.It consists of laser, laser detector and measuring circuit.Laser sensor is a new measuring instrument.
6. Hall
Hall sensor is a kind of magnetic field sensor made according to hall effect.Hall sensors are divided into linear hall sensors and switching hall sensors.The linear hall sensor is composed of hall element, linear amplifier and emitter follower.Switching hall sensor is composed of voltage regulator, hall element, differential amplifier, schmidt trigger and output level, which outputs digital quantity.

Principles of partial sensor applications
1. Resistance type: when the metal conductor is mechanically deformed by external force, its resistance value changes with the change of mechanical deformation
2. Hall: change due to the hall effect (hall effect: a metal or semiconductor wafer placed in a magnetic field generates an electromotive force perpendicular to the direction of the current and magnetic field when it passes through).

 Английский
Английский  Китайский
Китайский  Немецкий
Немецкий  Корейский
Корейский  Японский
Японский  Farsi
Farsi  Portuguese
Portuguese  Russian
Russian  Испанский
Испанский